Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins induce microRNAs that suppress multiple autophagy genes - Kumar - 2020 - International Journal of Cancer - Wiley Online Library

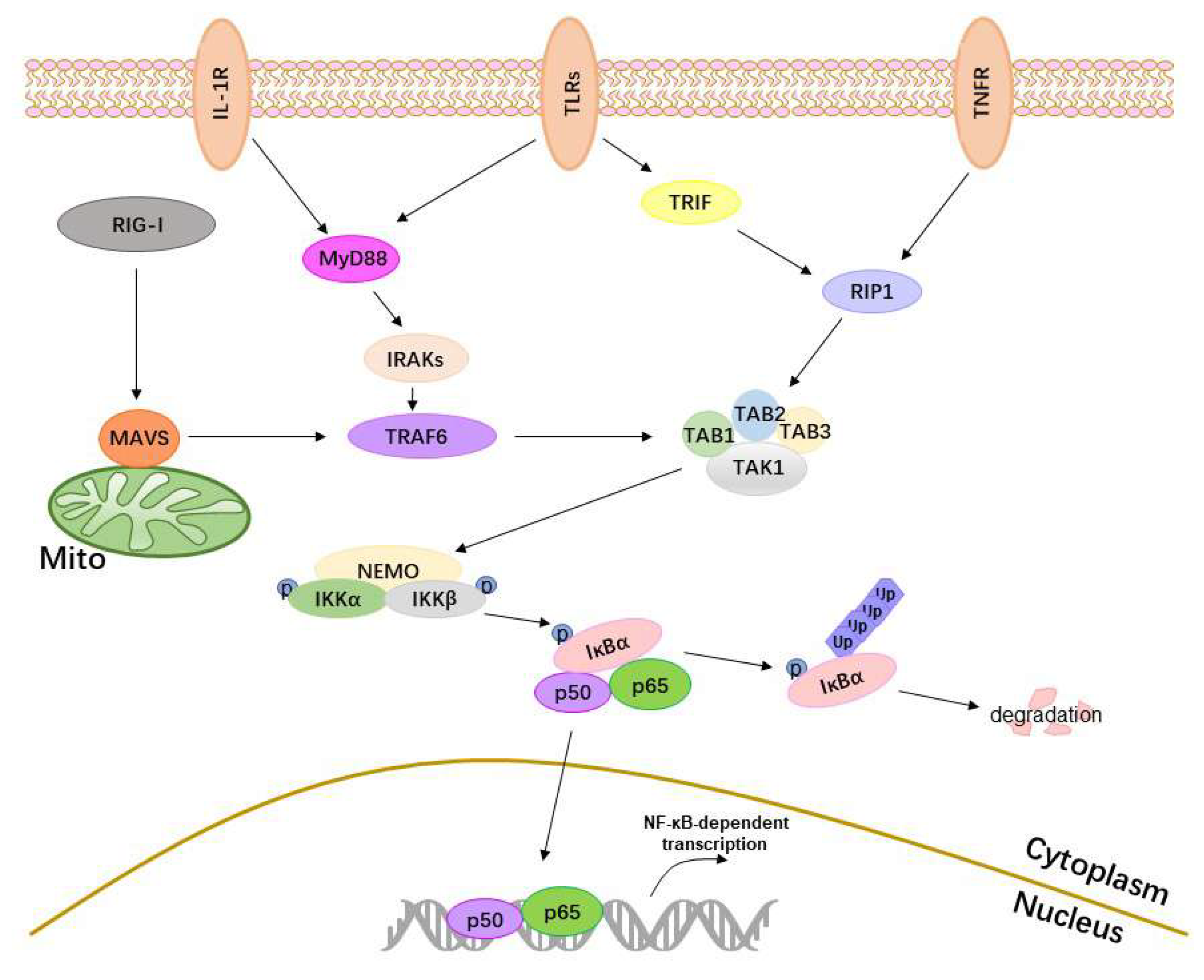
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Merkel cell polyomavirus is one candidate IL-1 trigger in LCH. Merkel... | Download Scientific Diagram

Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen targets the NEMO adaptor protein to disrupt inflammatory signaling. - Abstract - Europe PMC
![PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/29b5c89417b4ce10560da7d431ce9b0fdc05503b/73-Figure1.13-1.png)
PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection Induces an Antiviral Innate Immune Response in Human Dermal Fibroblasts | Journal of Virology

Frontiers | From Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection to Merkel Cell Carcinoma Oncogenesis | Microbiology

Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins induce microRNAs that suppress multiple autophagy genes - Kumar - 2020 - International Journal of Cancer - Wiley Online Library

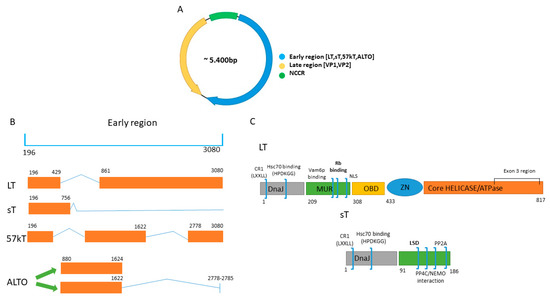
Characterization of functional domains in the Merkel cell polyoma virus Large T antigen - Houben - 2015 - International Journal of Cancer - Wiley Online Library

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Morphologic and immunophenotypical features distinguishing Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive and negative Merkel cell carcinoma | Modern Pathology

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection Induces an Antiviral Innate Immune Response in Human Dermal Fibroblasts | Journal of Virology

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

PDF) Modulation of Innate Immune signaling by the small T antigen of Merkel cell polyomavirus -the causative agent of Merkel cell skin cancer

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology
Structures of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus VP1 Complexes Define a Sialic Acid Binding Site Required for Infection

HSV-1-induced activation of NF-κB protects U937 monocytic cells against both virus replication and apoptosis | Cell Death & Disease