53BP1 and g -H2AX colocalize in persistent or spontaneous DNA damage... | Download Scientific Diagram
Pharmacological boost of DNA damage response and repair by enhanced biogenesis of DNA damage response RNAs | Scientific Reports
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of γH2AX and 53BP1 for Analyzing the Formation and Repair of DNA Double-strand Breaks | Protocol

Assessment of DNA damage by 53PB1 and pKu70 detection in peripheral blood lymphocytes by immunofluorescence and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy | SpringerLink

Regulatory cross-talk determines the cellular levels of 53BP1 protein, a critical factor in DNA repair - Journal of Biological Chemistry

NuMA accumulates at DNA damage sites. (a) Immunostaining for NuMA and... | Download Scientific Diagram
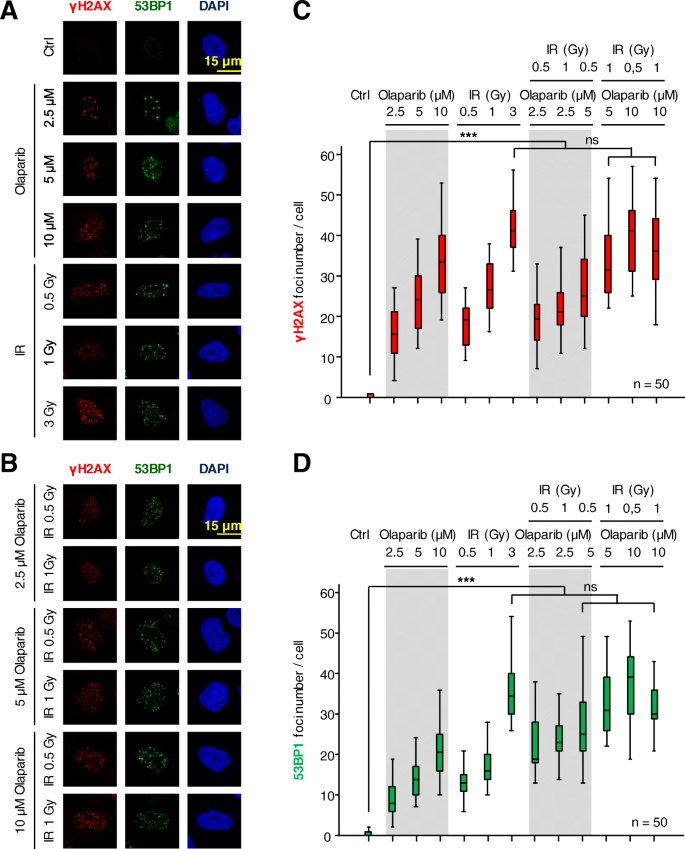
Olaparib and ionizing radiation trigger a cooperative DNA-damage repair response that is impaired by depletion of the VRK1 chromatin kinase | SpringerLink

The p53-binding protein 1-Tudor-interacting repair regulator complex participates in the DNA damage response - Journal of Biological Chemistry

FAM35A associates with REV7 and modulates DNA damage responses of normal and BRCA1‐defective cells | The EMBO Journal

A combined γ-H2AX and 53BP1 approach to determine the DNA damage-repair response to exercise in hypoxia - ScienceDirect

Immunofluorescence staining of markers of DNA damage response: 53BP1... | Download Scientific Diagram

Immunofluorescence staining of markers of a DNA damage response: 53BP1 (green) and gamma-H2AX (red) in human osteoblast-like U-2 OS cells on fresh and aged C60/Ti composites with various Ti concentrations (low: 25%,

53BP1 Mediates Productive and Mutagenic DNA Repair through Distinct Phosphoprotein Interactions: Cell

Aging | A role of the 53BP1 protein in genome protection: structural and functional characteristics of 53BP1-dependent DNA repair - Full Text
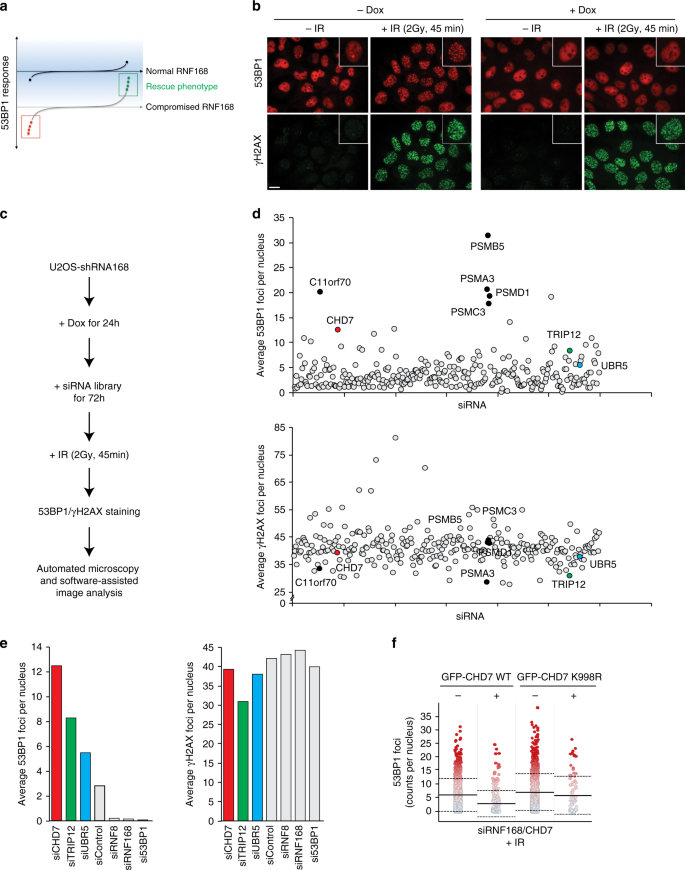
CHD7 and 53BP1 regulate distinct pathways for the re-ligation of DNA double-strand breaks | Nature Communications